The Road to Responsible Data
May 26, 2022

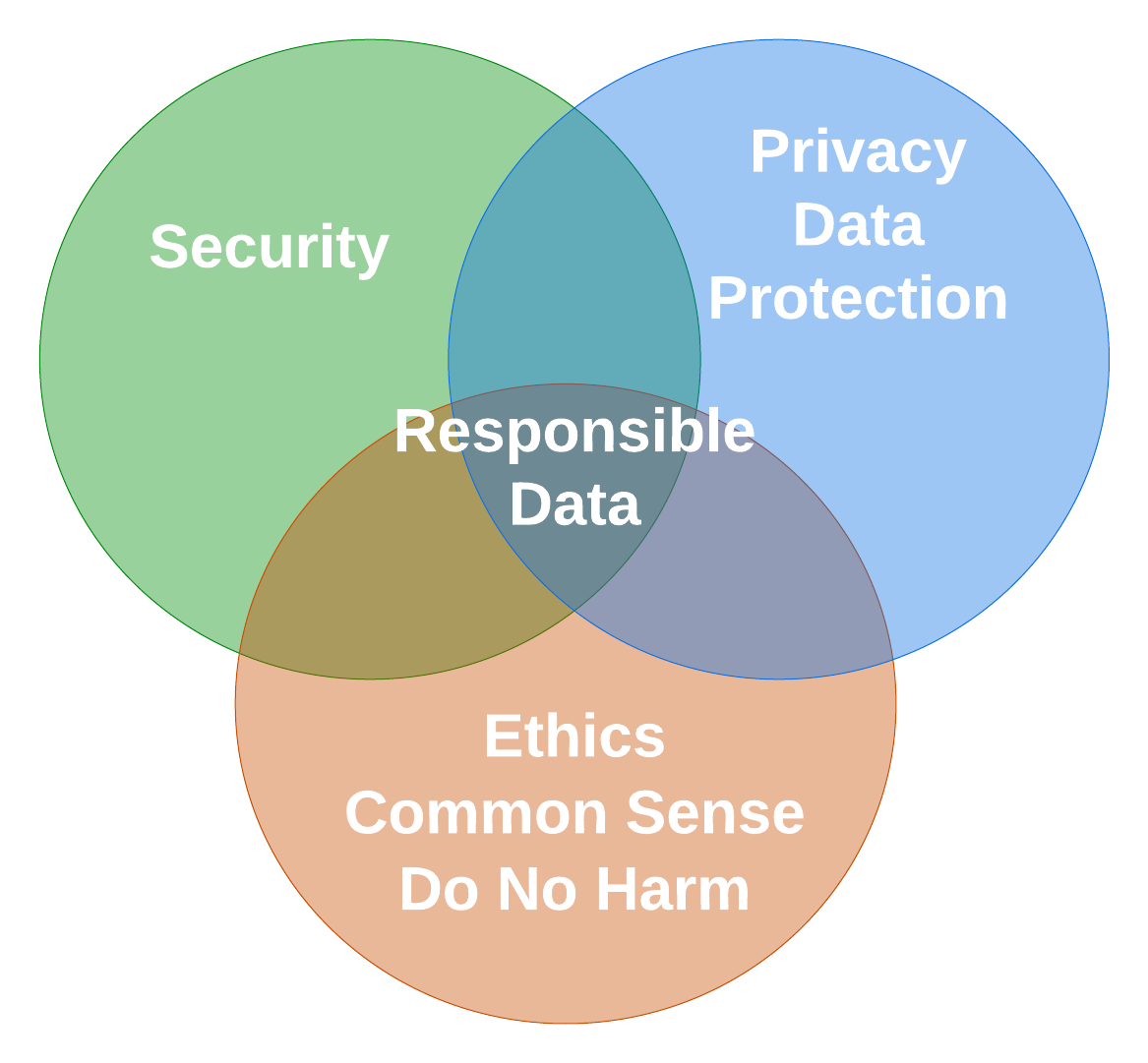
Responsible Data
- An approach for mitigating negative or unintended outcomes from implementing tech
- Openness and Transparency
- Focused on social impact of tech
- Risk and harms to individuals and society
- Proportional? Power imbalance?
- Can an org articulate why it's collecting data and what concrete benefits this will deliver to the data subjects?
Responsible Data
- An approach for mitigating negative or unintended outcomes from implementing tech
- Openness and Transparency
- Focused on social impact of tech
- Risk and harms to individuals and society
- Proportional? Power imbalance?
- Can an org articulate why it's collecting data and what concrete benefits this will deliver to the data subjects?

Why Do It? Who Does It?
- Tech has very real consequences
- Social impact and Theory of Change
- Getting ahead of regulation and legislation
- Corporate responsibility, brand, consumer benefits
- NGOs, big tech, academic, government

Use Case: Responsible Data for Children
Vanilla case: Children are an inherently vulnerable group with well-defined rights.
Principles:
- Purpose Driven
- Participatory (Transparent)
- Professionally Accountable
- People-Centric (Child-and-Family-Centric, but no P)
- Prevention of Harms Across Data Lifecycle
- Proportional (Does tech align with Purpose?)
- Protective of Children's Rights
In practice: Vaguely GDPRish, see Primero

Use Case: Responsible Biometrics
Uses:
- Identity (ID2020)
- Efficient aid and service delivery (fraud/duplication prevention), paired with blockchain!
Biometrics cannot be changed!
Leads to issues with privacy, security, and access.
Little regulation, the potential for abuse, and poor evidence of efficacy in programs.

The Road to Responsible Data: Overview
Privacy Data ProtectionPrimero
Downtown Boston
50 Milk St. | 16th floor
Boston, MA 02109 | +1-617-357-5233
Charlotte Metro
210 Delburg Street
Davidson, NC 28036-8634 |


BostonCharlotteNew York CityWashington DC