As technology advances, more secrets of our universe are revealed. Few are more important than how our brain works. Using our accumulated knowledge across multiple disciplines, we are making what would have seemed fantastical as little as 100 years ago an achievable reality. That reality is a Brain Machine Interface. This technology-meets-biology works by leveraging how neuronal activity and biological processes create signals that can be detected. Using various means of signal acquisition, we can feed the data gathered to machine learning and deep learning algorithms to extract the meaningful data. With this data, we can translate the useful brain signals to computer source code that can further operate a device or communicate with an application. There are many potentials for this technology - currently none more important than to aid people who suffer disabilities. Of course, as with any new technological advance, there will be difficulties with the actual steps of the process, as well as novel questions on ethics, morality, and potential dangers.

- Hans Berger to thank for first recording human brain activity with EEG
- Professor Jacques Vidal first to pioneer the field
- Fields in used in BCI:
- Neuroscience
- Signal processing
- Machine learning/Deep learning
- Computational intelligence
- Cognitive science
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Physics
- Neuromodulation, Neuroprostetics, Brain Computer Interface
Q: What is a BCI?
A: System that measures and uses signals produced by the central nervous system
Q: What is its purpose?
A: Detect user intention and translate that to user intent via a machine
Q: What are the parts?
A: Signal Detection, Feature Extraction, Feature Translation, Device Output
The brain operates on about 20 watts, equivalent computer is about 24 million watts
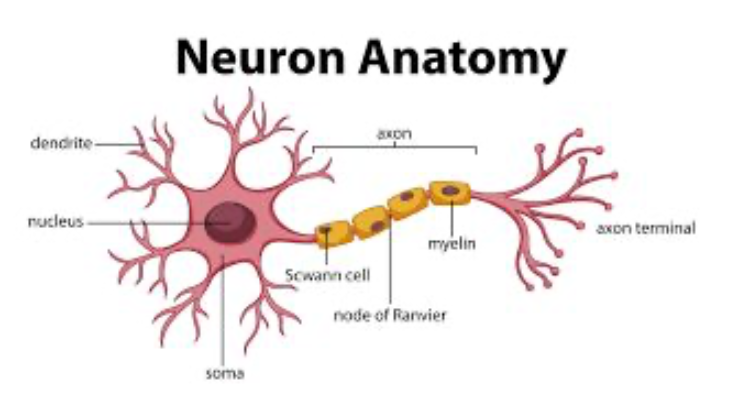
Cell body (aka Soma) - Does cell stuff
Dendrite - Receives neurotransmitters
Axon - Directs electrical signal
Axon Terminal - Releases neurotransmitters
Action Potential - All or nothing
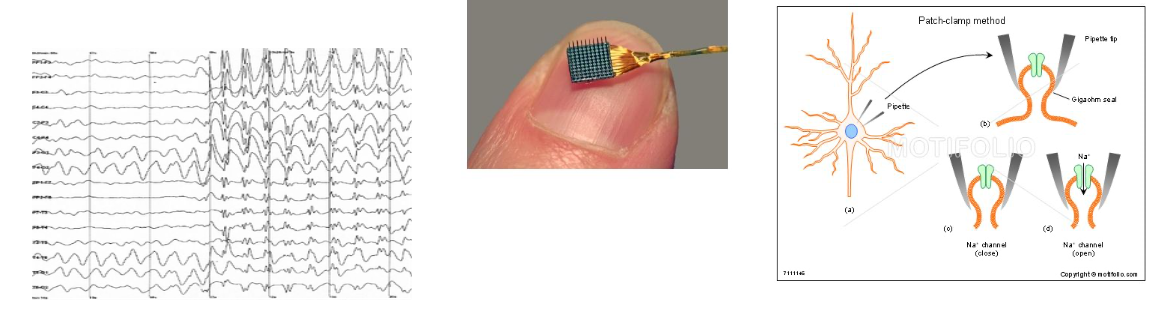
- EEG (electroencephalography)
- fMRI (Functional magnetic resonance imaging)
- ECoG(electrocorticography)
- Local Field Potential
Machine Learning: Uses algorithms to parse data, learn from that data, and make informed decisions based on what it has learned
Deep Learning: Subset of machine learning that learns by structuring algorithms in layers to create an "artificial neural network” that can learn and make intelligent decisions on its own using unstructured and unlabeled data sets
- Motor impairments
- Speech / Spelling device
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
- Robotic / Prosthetic movement
- 2 dimensional mouse cursor control
- Gaming
Signal acquisition hardware
- More comfortable external electrodes
- Minimize the invasiveness
- Which signal recording devices are most appropriate in certain circumstances
Validation and Dissemination
- How effective is the BCI
- How affordable is it
- How much impact on the user’s quality of life
Reliability
- More focus on making the signals recorded stronger and more consistent
- Use more signals to create more robust mapping
- Even more complex AI systems being worked
- Exploitation
- Losing one’s sense of self
- Human divide

